IBM Pairs Xilinx FPGAs to POWER8 to Create an Education Cloud Service
Today IBM has announced “SuperVessel”, an OpenStack based cloud service that enables students and developers to develop applications on a POWER 8 based infrastructure. What makes this cloud service interesting is the announcement that Hemant Dhulla, Vice President of Data Center and Wired Communications for Xilinx made:
Xilinx is delighted to have been chosen as the provider of FPGA accelerators for the IBM SuperVessel cloud. FPGA-based compute acceleration is a critical part of the OpenPOWER Foundation vision to handle demanding workloads in the most cost and power-efficient way. For this reason, a CAPI-enabled Xilinx FPGA is attached to every IBM POWER8 node in the SuperVessel cloud. The research and development being done in the SuperVessel is helping to define the future of heterogeneous computing.”
FPGAs, or field-programmable gate arrays are traditionally used to perform a specific algorithm in hardware. The result is a bulky and expensive chip (produced in low quantities) that runs a certain algorithms at very high speed and low latency.
Offloading some processing tasks to a specialized chip is certainly nothing new. APUs are CPUs that offload some of their tasks to integrated GPUs. But quite a few parallel algorithms run fast but pretty inefficiently on GPUs. In many cases, an FPGA uses a lot less power.
Intel has been delivering “customized” Xeons to large customers such as Amazon en Facebook, and has been promising that it will integrate Altera FPGAs inside certain Xeons. Intel recently bought Altera for $16.7 Billion.
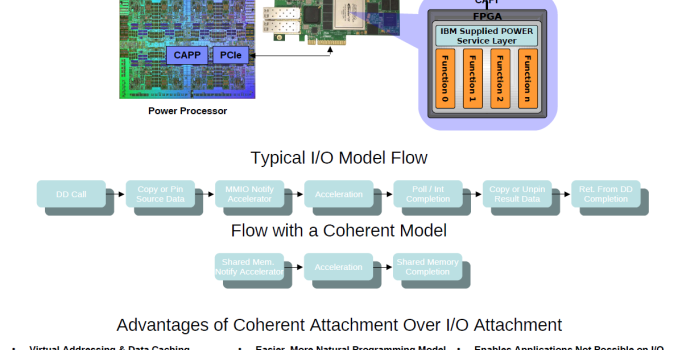
But IBM seems to have beaten Intel to the FPGA punch with CAPI, the POWER8’s Coherent Accelerator Processor Interface. IBM does not integrate FPGA inside the POWER8 package (yet), but communicates coherently over the PCI express interface.
The most interesting fact about “Supervessel” that is IBM has managed to make a cloud service that makes ample us of – traditionally expensive – FPGAs, and that the necessary software is in place to make it relatively easy to make use of those FPGAs. What software did IBM implement to make offload some of the processing work to the Xilinx FPGAs? Unfortunately, so far we only saw the press release and it is very light on technical details. Nevertheless, it is interesting to note that the OpenPOWER Foundation is making a lot of progress in very little time – it was founded only at the end of 2013.