In our series of Best Guides, here’s the latest update to our recommended CPUs list. All numbers in the text are updated to reflect pricing at the time of writing (29-Aug). Numbers in graphs reflect MSRP.
Best CPUs, August 2017
Sometimes choosing a CPU is hard. So we’ve got you covered. In our CPU Guides, we give you our pick of some of the best processors available, supplying data from our reviews.
| CPU Recommendations: August 2017 |
| AMD |
Segment |
Intel |
Ryzen 7 1800X
Ryzen 7 1700 |
$431
$300 |
Peak Gaming / VR |
$325
$337 |
Core i7-7740X
Core i7-7700K |
| Ryzen 5 1600 |
$210 |
Smart Gaming / VR |
$198 |
Core i5-7500 |
| Ryzen 3 1300X |
$130 |
Sub $700 Gaming |
$116 |
Core i3-7100 |
Athlon X4 960
Athlon X4 860K |
?
$66 |
Sub $500 Gaming |
$85 |
Pentium G4560 |
A12-9800 + AM4
A10-7890K + FM2+
A10-7860K + FM2+ |
$111
$143
$96 |
Integrated / eSports |
– |
– |
| Threadripper 1950X |
$1000 |
CPU Workstation |
$1000 |
Core i9-7900X |
Threadripper 1900X
EPYC 7251 |
$549
$475 |
Memory Workstation |
$213 |
Xeon W-2123 |
| Raven Ridge APUs |
|
One to Watch |
|
Core i9-7980XE
Core i7-8700K
Core i3-8100 |
The majority of our recommendations aim to hit the performance/price curve just right, with a side nod to power consumption as well.
If ‘peak’ is to mean ‘money no object’, then we typically suggest some of the most expensive processors, regardless of platform cost. Under this heading, the Ryzen 7 1800X at $499 (MSRP) represents the best AMD has to offer on a mainstream platform, with the highest frequency in the AMD Ryzen 7 range, eight cores, and consistent memory performance. There isn’t much headroom for overclocking beyond 4.0 GHz, but as a single or dual GPU solution AMD has you covered. The AM4 motherboard platform is also now mature, with the latest AGESA updates showing some good gains in performance. AMD has stated that they are committed to future AGESA updates to boost performance as well.
Users who still want a peak experience and feel comfortable with overclocking can instead save $170 from the list price by going after the Ryzen 7 1700, which is the same as the 1800X except for a slightly lower clock frequency. This processor can be overclocked to 1800X or near 1800X levels in most environments, allowing users to get another $170 on a graphics card, CPU cooler, memory or storage.

For users going down the Intel route, the new Kaby Lake-X based Core i7-7740X represents the top step for performance out of the box. The only way to get 4.5 GHz for any other processor is through overclocking. Similar to the AMD parts, this CPU supports up to two way SLI and up to 64GB of DRAM, but the downside here is that the X299 motherboards that this CPU requires start at almost double the average price, although they can be upgraded to larger Skylake-X CPUs for users with deeper pockets over the next few years.
The peak experience on Intel can also be had by the Core i7-7700K, a Kaby Lake-S processor that can hold a frequency close to 5.0 GHz with some overclocking, but can also be placed into a Z270 motherboard, reducing the system cost to get the same experience and putting more money aside for other components. As for a pure out-of-the-box gaming experience without overclocking, the Core i7-7740X still wins however.
For users that want to move beyond two GPUs in a truly money-no-object gaming and streaming and video editing environment, then it becomes a choice between AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper processors and Intel’s Skylake-X components. More on those later.
Virtual Reality on a Reasonable Budget: The Smart Gaming Choices
The Intel Core i5-7500 or AMD Ryzen 5 1600
For processors that still need to perform but do not blow a hole in the wallet, both AMD and Intel cater for this market actively. On AMD’s side, we’ve chosen the Ryzen 5 1600. This processor uses the same underlying technology and base as the higher-class Ryzen 7 processors, but removes some peak performance in workloads such as video conversion in order to be offered at a lower price point. It comes with six cores and twelve threads with a good out-of-the-box performance that can be pushed higher with a nice overclock. To save a few pennies, the retail version also comes bundled with a CPU cooler worth using.

Intel’s side of the fence is a bit fuzzier. The Core i5-7500 is what we’ve chosen here: a quad core processor without hyperthreading that will give a near-identical gaming experience to the Core i7 parts, especially in older games that rely on single thread performance. If that is all you care about, the Core i5-7500 (or i5-7400 to save a few more $) with a 200-series ecosystem and a beefy GPU will not disappoint. For a user that wants to process video, or do some heavy work, it might be worth cutting a couple of percent on that gaming performance and going for the AMD parts that offer twelve threads compared to Intel’s four. For heavy work with gaming, it’s hard to miss AMD in this price range when comparing the two.
Our suggestions for processors in $700 PCs get an update here on the AMD side, as since the last guide we have had AMD’s Ryzen 3 processors come to the market. These are quad core parts in the $110-$130 range, with the same features and nearly the same high frequencies as their Ryzen 5 and Ryzen 7 siblings, but aimed at this lower price. Out of the two Ryzen 3 processors, the 1300X gets the gold star by being a higher frequency out of the box, a larger XFR boost, and having plenty of room to overclock as well on the cooler provided.

The competition from Intel sits at the door with the Core i3-7100. The trade offs here are a higher single thread frequency, but only two cores with four threads rather than a full four cores. For some of the newer games, or for more multi-tasking activities, that could be of concern to users but for a cheap gaming system, the Core i3-7100 should have no issues with eSports-like titles or driving mid-range graphics cards. Some users might prefer going after something like the Pentium G4560, which is only a few MHz lower on frequency but has half the list price, which is why it sits in our next recommendation.
The Pentium G4560 is heralded as the diamond in the rough for sub $100 processors. It comes out of the gate with a sizeable 3.5 GHz frequency, two cores, four threads, and a list price of $64. In previous generations, a chip like this would be almost double the price if not more, which makes it an interesting purchase for users who rely on cheaper components for something like a $500 gaming system. Technically this CPU is an OEM processor, so finding stock might be tricky, or the fact that it usually sits at $80 or so at retail, but even at that price it still becomes the processor of choice.

For now, AMD’s Ryzen processor family and newest silicon does not drop down to this price bracket. However since our last CPU guide, AMD has officially released their Bristol Ridge processors to market. These were available in OEM pre-built PCs for the last year or so, but now come to market as the best of AMD’s previous generation of products. For users looking at investing in a discrete graphics solution to pair with an AMD Bristol Ridge CPU, the Athlon X4 960 sits at the top of the CPU options here, marking an upgrade over our last Q2 recommendation by moving to AM4 motherboards and support for DDR4, as well as performance improvements.

AMD stated these CPUs should be on shelves by August 18th, and we’re waiting to get one in ourselves for testing. Ultimately the X4 860K is easier to purchase, but relies on the older FM2+ based motherboards, which is why it still appears in our recommendations.
Play Now, Play Later: Gaming on Integrated Graphics
The AMD A12-9800, AMD A10-7890K or AMD A10-7860K
Building a smaller or cheaper gaming system, either as a full-time PC or as a precursor to buying a large discrete GPU, AMD’s new Bristol Ridge processors are the best options. These are updates over the previous generation Kaveri processors, and use the latest AM4 platform for PCIe 3.0 support as well as DDR4 and the latest audio/networking controllers. The A12-9800 sits at the top of this processor list, and should be around $120 depending on location.

Users who want to cut a few more dollars off the build, or depending on the availability of the new A12 processors, can still look at the Kaveri A10 parts. The A10-7890K is the best processor in that range, although the A10-7860K is practically as-good but at a lower price point. These parts still use DDR3 memory which might require diving into the pre-owned bin, but paired with some fast memory and they can still tackle a good number of modern games at low-to-medium settings very well.
Not many users take the line of integrated graphics because GPUs like the RX460 can be relatively cheap (when people aren’t mining) and usually outperform what is on offer. Nonetheless, almost all mainstream CPUs come with integrated graphics for several reasons: invest now in a good CPU then later in a GPU, or the amount of space limited in the system is small, or features such as QuickSync or OpenCL are needed for the user workloads.
For users who want it all, the best of the best, or actually need lots and lots of compute power, then both AMD and Intel want to sell you some clever sand. Since our last guide, AMD launched its new Ryzen Threadripper processors and X399 motherboard platform, offering up to sixteen of their new Zen cores, up to 32 threads, sixty PCIe lanes to play with, and a high turbo frequency. The Threadripper 1950X is the top processor here, retailing at $999, and in our testing stretched out a sizeable lead on almost all of our hardcore throughput tests. The Threadripper CPUs are based off of AMD’s server products, and the way they are manufactured does mean that a few compute edge cases need additional optimization, but AMD has attacked this market hard with a product very few people were expecting. The 1920X is also available, with 12 cores and hyperthreading for $799, also with 60 PCIe lanes.
The recent set of high-end CPU releases means there is a lot of choice, as well as variation in performance and price. Intel’s current top offering is a 10-core Core i9-7900X, which pushes through Intel’s traditional conservative frequency and power ratings to give a very fast multi-core processor that also bundles in compute features such as AVX-512. The Core i9-7900X is the current top component of Intel’s Skylake-X CPU line, with a full set of 44 PCIe 3.0 lanes and takes advantage of the new X299 chipset for motherboards to take advantage of more controllers. Intel also offers two other CPUs in this range, with reduced core counts and reduced PCIe lane offerings.

Both platforms have tradeoffs here. AMD has the raw core count and more PCIe lanes, at the expense of a few watts. Intel instead has AVX-512 and higher single thread performance, but has fewer PCIe lanes (which decrease with cheaper CPUs). Both systems use quad-channel DDR4 memory, and both have different approaches to how each of the cores talk to each other: Intel’s new network Mesh allows for scalability within one large piece of silicon, while AMD’s multi-silicon strategy uses their new Infinity Fabric for scale. We’ve seen both methods have upsides and downsides, along with improvements and regressions.
Some workloads just need lots of memory. The more memory in a system, the better – even with DRAM prices currently skyrocketing, some compute tasks just need memory. Both of AMD and Intel’s best consumer platforms can accept up to 128GB of DRAM, suggesting that it comes down to the cheapest processor on each: Intel’s Core i7-7800K is around $350, while AMD’s Threadripper 1900X will be at $549 when it comes out at the end of the month.
For users looking to get serious about memory capacity, the tables turn the other way when we look at the enterprise platforms. Both AMD and Intel have launched new server processors in the last few months, so pricing and availability become strong elements into our recommendations here.
The winner in what we recommend falls at AMD’s EPYC ecosystem, which can run up to 2TB per socket when using 128GB LRDIMMs. Those memory modules run at $4000+ each if you can find them, ensuring the $64000+ cost of the DRAM is more of a consideration than what the processor cost is. The availability of EPYC platforms from the OEMs is still a work in progress however: unless you want to deploy a substantial number of servers, it’s going to take some time (several months) before EPYC is fully deployed to customers other than the big cloud providers. Even the low-end CPUs that support 2 TB per socket, priced around $450, are not ‘freely’ available with AMD and OEMs focusing on the higher margin parts first.

By comparison, Intel’s partners are shipping new Xeon platforms today. These come in two variations: the Xeon-SP platform based on Xeon Bronze, Xeon Silver, Xeon Gold and Xeon Platinum, and also the Xeon-W platform that reuses the LGA2066 socket from the consumer space. The Xeon-W 2123 processors, with their cheaper motherboards, can support up to 512GB of DDR4 memory, and are destined to find their way into retail packaging. The Xeon-SP processors start support at 768GB of DRAM, although to get special 1.5 TB support versions, these will cost ~$3000 (list price) above the regular versions and come via OEMs only. These double memory parts start in the Xeon Gold range, and the base versions vary around $3000 anyway.
The 2017 August CPU Market Roundup
So far the first half of this year has been mildly insane. Back in 2016, we had the best part of 1.5-2 platform launches and it was a quiet year on the CPU side. So far this year we have had three or four launches, with another few in the pipeline to come. With Kaby Lake, Ryzen 7 and Ryzen 5 out of the way, in comes Kaby Lake-X and Skylake-X to the party, followed by Skylake-SP, Threadripper, EPYC, and potentially more still on the invite list later this year such as Intel’s 8th Generation.

For consumers, it can be a fun time. With new platforms comes an opportunity to upgrade, either through the increase in performance or just because you want the latest and greatest. The idea is that the newest processors are more performant, or lower power, or fit into a particular niche better (and hopefully are the same or lower cost overall). For users who wanted to invest in AMD this year, Ryzen has been a good offering and ThreadRipper is aiming at the multi-core market. For users looking to upgrade that i7-2600K or i5-2500K, Intel is trying hard to tempt them with Kaby Lake processors and even Kaby Lake-X, with the best part of 25-35% IPC and some extra MHz as well. For anyone that wanted a 10-core CPU and thought $1721 was too much for the i7-6950X, Intel has you covered with the Core i9-7900X at $999-$1049 now as well.
Our big CPU reviews for 2017 have covered all the launches so far, and well worth a read,
Intel 2017 Reviews
AMD 2017 Reviews
In the pipe coming in the next few weeks include our AGESA retest on Ryzen, Skylake-X Gaming analysis, hopefully some reviews of the 1900X/7920X that should be going to market this week. and we’ve put in a request for some EPYC and Xeon-W processors as well.
One of the overriding issues so far this year worth mentioning is platform maturity. With new platforms come new challenges, and as far as we understand, extreme deadlines. Motherboard manufacturers, for both AMD and Intel, have had to rush through some of the production of their initial motherboards at launch. When we reviewed Ryzen 7 and Kaby Lake-X, both of those reviews did not have gaming results due to erroneous results on young hardware. At this point we expect both platforms to be running smoothly, but as an indication that this year is about time to market, it’s a big one to note for early adopters (and reviewers that end up wanting to throw products out a window).
Prepare for Processors: Ones to Watch
AMD Raven Ridge, Intel Core i9-7980XE, Intel Core i7-8700K, Intel Core i3-8100
Despite this year being one of the busiest on record for CPU launches, the finishing line is almost in sight. AMD’s focus between now and the end of year, aside from the Threadripper 1900X coming out at the end of August, is going to be on their Raven Ridge laptop components that pair four Zen cores with a Vega GPU. We will see desktop versions of these processors, but not until the end of the year at the earliest.
Intel still has some bandwidth coming up to make life on the desktop interesting, however. The rest of the Skylake-X processors, from 12 to 18 cores, are set to launch in the next couple of months. Intel has stated that the 12-core 7920X should be at the end of August, with the 14 and 16-core parts in October. The full 18-core is likely to hit our scene around the same time as well. These parts will compete against AMD’s 16-core Threadripper 1950X, although AMD will have a price advantage: Intel’s 16-core already has an announced $1700 price tag, compared to $999 for AMD. When we get the parts for review, it will be an interesting showdown.

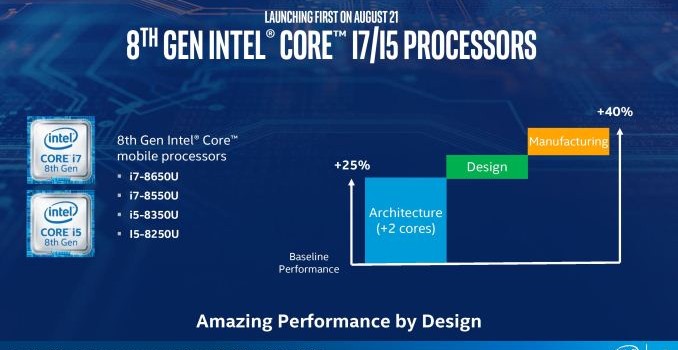
The other coin in Intel’s launch schedule is going to be the new 8th Generation coming to Desktop. We’ve already reported that the Intel launched the 8th Gen with a quartet of refreshed laptop processors, but these were refreshes of previous generation parts with double the cores. Users are expecting the desktop components to be new designs (‘Coffee Lake’) and as we reported on in the last couple of weeks, Intel is telling partners that the top Core i7-8700K processor will have six cores, meaning that after a decade of Intel’s mainstream platform offering quad cores, it marks a long-awaited step up to hex-cores. Out of the data we obtained and verified last week, the interesting component for me was the Core i3-8100. This will be a quad-core processor, similar to the current Core i5 parts, but should come in around $120. This level of base performance, on paper, should be a nice entry level processor compared to the dual cores that are slowly limiting what a non-gaming PC is now required to do.
Perhaps the downside to this 8th Gen launch will be the socket and motherboard situation: these new processors are expected to be in the LGA1151 form factor, the same as the current generation, but will require new 300-series motherboards that will not be backward compatible with older processors. That in itself is not a new thing – we are used to having Intel refresh platform capability every two generations, however we typically get a new LGA form factor as well as a jump in capability/reduction in process node. This will be Intel’s third desktop processor on 14nm, breaking that cycle, and no official word has been given to whether the new chipset has new features, leaving some of us to wonder if backward compatibility isn’t possible due to product segmentation. The big fuss around a new process node, as well as a new socket form factor or change in the form factor naming helps ease the transition from one platform to another when they are not backward compatible. Intel should understand this from previous experience. If it is still named LGA1151, then it only adds to the confusion and becomes one less way to differentiate between different product families.
Links to Other Guides