AMD’s 2016-2017 x86 Roadmap: Zen Is In, Skybridge Is Out
AMD’s CTO Mark Papermaster just left the stage at AMD’s 2015 Financial Analyst Day, and one of the first things he covered was AMD’s CPU technology roadmap for the next couple of years.
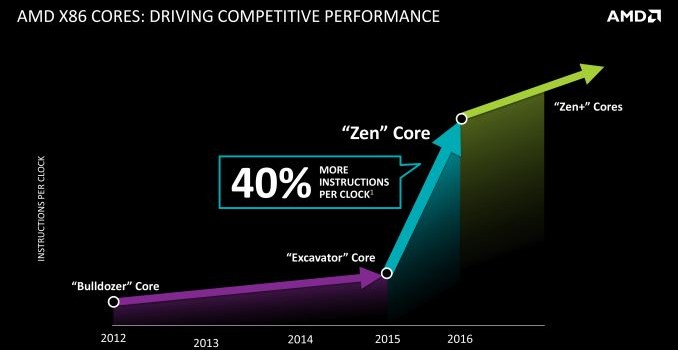
The big question on everyone’s mind over the last year has been AMD’s forthcoming x86 Zen CPU, developed by Jim Keller’s group, and Papermaster did not disappoint, opting to address the future of AMD’s x86 plans first and foremost. AMD is not releasing the complete details on Zen until closer to its launch in 2016, but today they are providing some basic details on the CPU’s abilities and their schedule for it.
In terms of features, AMD once again confirmed that they’re aiming for significantly higher performance, on the order of a 40% increase in Instruction Per Clock (IPC) throughput. In a significant shift in threading for AMD’s x86 CPUs, Zen will also shift from Bulldozer’s Clustered Multithreading (CMT) to Simultanious Multithreading (SMT, aka Intel’s Hyperthreading). CMT is the basis for Bulldozer’s unusual combination of multiple integer cores sharing a single FPU within a module, so the move to SMT is a more “traditional” design for improving resource usage, and it means Zen will similarly have a more traditional resource layout. AMD is also labeling Zen’s cache as a “high-bandwidth, low latency cache system,” though at this time they aren’t quantifying just how that differs from the Dozer family’s cache.
Meanwhile AMD has confirmed that Zen will be shipping in 2016, and that it will be produced on a yet-to-be-named FinFET process. Our bet would be that AMD continues to use traditional partner (and spin-off fab) GlobalFoundries, who will be ramping up their 14nm equipment for next year as part of their licensing/partnership with Samsung to implement Samsung’s 14nm FinFET process. Zen at this time is AMD’s priority, to the point where the company is willing to push back the ARM K12 in order to get Zen out the door first.
Desktop users will be happy to know that the first Zen processor out the door will be AMD’s high-end desktop CPU (AMD was very deliberate in this, it’s not an APU). AMD will be aiming high and then cascading Zen down into APUs and lower-end products.
Said Zen CPU will use a new AMD platform – AM4 – which will also support DDR4. Unlike the Dozer family, all of AMD’s desktop CPUs will use the same AM4 platform/socket, so when AMD does ramp up their Zen APU, it too will be on AM4 and not its own socket, simplifying the process.
Finally, AMD’s roadmap for Zen over 2016-2017 calls for further improved Zen cores, “Zen+”, later on. Though the biggest jump for AMD comes from the transition from Dozer to Zen, the company is looking to push the envelope on IPC harder than they did with the Dozer family, projecting a higher increase in IPC over time than what we saw with the Dozer parts.
As for what this means for single-threaded performance, that remains to be seen. After having chased a lower-IPC/higher-clockspeed strategy in an attempt to do something different from Intel – the AMD that designed Bulldozer thought it wise not to try to beat well-funded Intel at their own game – the focus on higher IPC is arguably the correct move to make as the laws of physics have continued to keep 5GHz+ clockspeeds from being efficient enough to be practical. That said, single-threaded performance is a combination of IPC and clockspeed, so to be competitive with Intel AMD needs to deliver higher IPC while maintaining relatively high clockspeeds, and the latter is not something AMD is disclosing this early in the process.
Finally, we’ll note that this roadmap is empty of any mentions of project Skybridge. CEO Lisa Su has commented that AMD has decided to change their focus away from Skybridge based on customer feedback. Customers were telling AMD that they didn't necessarily need socket compatible solutions, so AMD is going to work on differentiated solutions. That said, given that Skybridge was announced last year and planned for 20nm, I suspect that it has also become a victim of the short lifespan (and underperforming nature) of 20nm, leading to it being downplayed in favor of 14nm prodcts.
Meanwhile also absent was any further mention of AMD's Cat cores. Zen would appear to be AMD’s top-to-bottom x86 core, a significant departure from an AMD who previously wanted separate designs for the 10W-100W market and sub-10W markets.